Is WeChat safe? A complete privacy and security guide

WeChat is a popular messaging app developed by Chinese tech giant Tencent that combines chat, payments, and more into one platform. As it handles your personal data and your financial information (if you use its payment features), it’s important to understand WeChat's approach to data collection and sharing and the security measures it uses.
For parents, it’s also good to know who can contact your child on the app, what information they can share, and what other users can see on their account.
This guide covers all of the above, and offers tips on how you can better protect your privacy while using the app. We also compare WeChat to several other messaging apps, so you can pick the best one for your needs.
Is WeChat safe?
WeChat is a legitimate app that’s available through the Apple App Store and Google Play Store, which both review apps for policy compliance and known security risks before listing them and perform automated and manual checks on updates.
However, like any social app, users can be exposed to potential dangers if WeChat isn’t used carefully. Scammers on the platform may send phishing messages, link to untrustworthy websites, or impersonate trusted contacts to try to obtain personal or financial information.
While these risks are common across social platforms, WeChat has put several security measures in place to help protect users.
WeChat data encryption and security infrastructure
To encrypt data, WeChat uses a proprietary protocol called MicroMessenger Transport Layer Security (MMTLS), which is a modified version of standard TLS. While it is designed to serve a similar purpose as TLS, it departs from widely adopted implementations in several ways. In a study, CitizenLab researchers found that some of WeChat’s cryptographic changes to TLS may introduce weaknesses and that MMTLS hasn’t historically provided forward secrecy in some observed implementations. This means if someone ever gained access to a session key, they could potentially read older data that was encrypted with that same key.
WeChat states that it uses 256-bit Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) encryption to secure data in transit between your device and its servers, as well as while stored on its servers. AES-256 is a widely trusted, industry-standard encryption algorithm used by governments and security professionals to protect data from interception. However WeChat doesn’t use end-to-end encryption (E2EE). With E2EE, encrypted messages or calls can only be decrypted on the intended recipient’s device; the service provider can’t access the contents of your communication.
That said, according to WeChat, it doesn’t permanently record the content of messages on its servers, unless you or the recipient favorite a message or add it as a group notice. According to WeChat’s disclosures, content that doesn’t fall under these exceptions is typically retained for limited periods, such as:
- Text messages: Up to 72 hours.
- Images, audio, videos, and files: Up to 120 hours.
How attackers target WeChat users
Attackers target WeChat users in several ways. One of the most common approaches involves unsolicited messages that link to malware downloads or phishing pages. Scammers may also pose as WeChat support or trusted businesses to pressure you into giving up personal information or sending payments that you don’t actually owe.
Note that datasets linked to WeChat user information have been exposed in the past, rather than through confirmed breaches of WeChat’s internal systems. Attackers can use the exposed data from these incidents to send highly targeted phishing messages inside and outside WeChat, or to impersonate legitimate contacts.
There are also additional risks that WeChat users should be aware of, including:
- Misleading or cloned Mini Programs: Some Mini Programs imitate legitimate services and may misuse their permissions to collect information or expose users to malware.
- Fake or look-alike messaging apps: Malicious apps can imitate well-known chat services like WeChat and hide spyware designed to steal contacts, files, and other sensitive data.
Can WeChat be hacked?
WeChat, like any online service, can be hacked, although large-scale attacks are uncommon, and no major platform-wide breaches have been publicly documented. As previously mentioned, there have been cases where WeChat-linked records were exposed through misconfigured or unsecured third-party databases. These incidents didn’t involve WeChat’s internal servers but still placed user information at risk.
Individual accounts are far more likely to be compromised than WeChat itself. If someone gains access to your device or your login information, they can directly see your recent messages and other activity.
They may also impersonate you, contact your friends or family, request money, or attempt to move conversations to other platforms to share malicious links with fewer restrictions. In some situations, attackers may try to take over additional accounts that use the same phone number or email address.
Because account protection on WeChat relies mainly on device security and control over your phone number, keeping your device secure, maintaining OS updates, and avoiding suspicious links or downloads helps reduce the chance of someone gaining access to your WeChat account.
Is WeChat safe for children?
WeChat isn’t designed specifically for children, but it does allow minors to use the platform with parental or guardian consent, in line with local age requirements. As such, here are some considerations to keep in mind:
- Children can be contacted by strangers through friend requests, group chats, or shared links.
- WeChat lets users hide chats, which makes it possible for kids to keep certain conversations out of view from parents.
- Kids can use WeChat Pay (the app’s built-in payment feature) to send money, make purchases, or respond to payment requests without understanding the risks.
- WeChat allows users to send documents, images, and other files. Unmonitored file sharing could expose kids to inappropriate content or harmful downloads.
- Users can share their real-time location with contacts, allowing children to share their current location.
- Children can be more likely to click on untrustworthy links, accept unknown contacts, or share personal information.
The parent or guardian must also acknowledge WeChat’s Privacy Policy. In certain regions, WeChat may require a parent or guardian to verify a payment card, such as a Visa credit/debit card, to show that they consent. These card details are processed by a third-party payment processor and your card data is not stored or bound to your account.
This Privacy Policy states that WeChat doesn’t knowingly collect personal information from children without this consent. It asks parents or guardians to contact the platform if they believe a child’s information has been collected so the data can be reviewed and removed. It’s also important to note that WeChat doesn’t allow you to change your birthdate after registration. This is to comply with local laws and regulations.
Keep in mind that WeChat offers Guardian Mode, a set of password-protected parental controls. Once turned on, the account can only add friends from group chats or via QR codes, strangers will be unable to view the account’s Moments posts (the equivalent of status updates), and various other features will be automatically disabled, such as Top Stories, People Nearby, and external links. Guardians can also manage access to Official Accounts (brand/business accounts) and Mini Programs.
WeChat privacy considerations
WeChat collects different types of information to support its various services.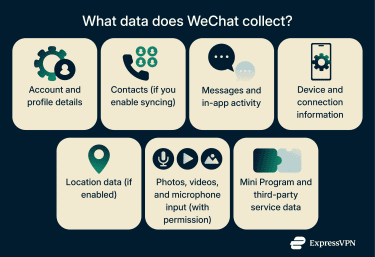
Here are the main categories of data WeChat collects:
- Account and profile information: Phone number, display name, profile photo, and any optional details you choose to add.
- Contacts (with permission): Information from your address book is accessible if you enable contact syncing.
- Messages and app activity: Communication content that passes through WeChat’s servers for delivery, as well as usage and activity data such as group participation, Moments activity, and interactions with in-app features.
- Device and connection data: IP address, device model, network type, and related log and diagnostic information.
- Location information (if enabled): GPS data or device-based location used for location-dependent features.
- Media and files (with permission): Photos, videos, microphone input, and camera access when using relevant features.
- Mini Program and third-party service data: Activity and information shared with Mini Programs or other services you access within WeChat, such as WeChat Pay. Note that these will have their own privacy policies and data collection practices, separate from WeChat.
WeChat asserts in its Privacy Policy that this information is used to provide its core services, maintain performance, improve features, and support account security. WeChat states that it does not retain personal information longer than necessary unless required or permitted by applicable laws, in which case certain data may be retained for longer periods or stored separately.
Mini Programs integrated inside WeChat
Mini Programs are small apps that run inside WeChat, letting you shop, make payments, play games, and use services without leaving the main app. They’re convenient, but they can also increase the amount of data you share and introduce additional privacy and security considerations.
Some Mini Programs handle sensitive information, including your financial information and health data. Despite the importance of this data, one 2021 review of 50 banking-related Mini Programs found that over half didn’t use strong data-encryption methods consistently at the time.
That said, WeChat has since put protections in place to improve how Mini Programs handle your data. Mini Programs can’t make unrestricted external web requests and must route network traffic through WeChat’s internal APIs, which allows WeChat to control which third parties they connect to and ensure those connections use encrypted HTTPS. WeChat also requires clear user permission before Mini Programs can access sensitive device functionality, such as the camera or location services.
You can reduce the risk of accidentally using unsafe Mini Programs by only accessing programs from WeChat’s built-in search feature or Discovery menu. Be cautious about opening Mini Programs through random QR codes or location-based features like the “Nearby Mini Programs” list, which shows programs based on your physical location.
Some Mini Programs also ask for extra permissions they don’t need, such as access to your contacts, location, or camera. Be sure to review permissions regularly to avoid oversharing information. If you’ve granted a permission for a one-off task, you can easily turn it off again afterward.
Does WeChat share data with Chinese authorities?
WeChat’s Privacy Policy states that it only shares user information with third parties when needed to provide the service or when required to follow valid legal requests. This includes situations such as complying with a court order, responding to a request from an authorised body, or addressing safety and security concerns.
For WeChat users, data is stored and processed outside mainland China. WeChat lists Singapore and the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region as its primary storage locations, with support teams in other regions such as the Netherlands that may have access to user information, subject to internal controls.
Because data is stored internationally, access may be governed by the legal requirements of multiple jurisdictions, depending on where teams operate, the location of the relevant user, and the information in question. In some circumstances, authorities with legal jurisdiction over the data may be able to request access. Note that WeChat doesn’t publish transparency reports, and its Privacy Policy doesn’t include examples of how often legal requests occur or what types of information may be involved.
Weixin accounts follow different rules under the Weixin Privacy Protection Guidelines. Weixin is the domestic version of the service and applies to users who register with a mainland China mobile number. It operates under separate terms and follows different data-handling processes and legal requirements.
How to better protect your privacy on WeChat
As with any messaging app, you may want to take extra steps to protect your privacy: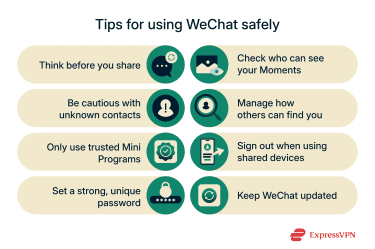
- Be careful with what you share: Avoid sending sensitive details like home addresses, ID numbers, or financial information through chats or unfamiliar Mini Programs.
- Be cautious with unknown contacts: Some users may send phishing messages or malicious links or attachments. Don’t open links or attachments from unknown users, and don’t give out personal information to anyone except those you explicitly trust.
- Only use trusted Mini Programs: Mini Programs can request broad permissions and follow their own privacy policies, which may differ from WeChat’s. Only use programs you trust and avoid giving permissions to sensitive data unless it’s clearly necessary.
- Use a strong, unique password: A long and complex password makes it harder for someone to access your account. Update it regularly and avoid reusing passwords from other apps or services (you can use a tool like ExpressVPN Keys to generate and store secure passwords).
- Review who can see your Moments: Moments can reveal more personal information than you intend. Make sure to adjust your privacy settings so only trusted contacts can view your posts.
- Control how people can find you: WeChat allows you to manage whether others can look you up using your phone number or WeChat ID; you can reduce unwanted contact requests by limiting this.
- Sign out on shared or borrowed devices: If you ever log in on a device that isn’t your own, make sure you sign out once you’re done to keep your messages and account secure.
- Keep your app updated: Updates often include security fixes that help protect your data. Be sure to install them promptly to reduce your exposure to known vulnerabilities.
App permissions you should disable
WeChat needs certain permissions to function, but some are tied to optional features that you may not be interested in using. Depending on how you use the app, here are some permissions you may be able to limit or turn off while keeping the basic messaging functionality intact:
- Location access (used for location-based tools in WeChat).
- Access to your contacts (used for syncing your device contacts with WeChat).
- Camera or microphone access (used for calls and voice/video messages).
- Photos or file storage access (used when sharing media).
- Background access that allows WeChat to run or connect (used for push notifications and some optional services).
Disabling some of these permissions may limit specific features, but basic text messaging can still work depending on your settings and device.
Should you use a VPN with WeChat?
A virtual private network (VPN) can’t change how WeChat handles or stores data internally, but it can help keep your connection private on insecure networks, such as public Wi-Fi hotspots. Such networks can be compromised by cybercriminals, allowing them to intercept the traffic of other users.
VPNs encrypt your internet traffic, making it unreadable to anyone attempting to listen in. They also hide your real IP address, which can help limit IP-based location tracking. If you turn off location sharing in WeChat and at the device level, this can further reduce how much precise location data the app can access.
Some VPNs can also block known trackers and malicious domains. ExpressVPN’s Threat Manager offers this protection without the need for any advanced setup.
WeChat vs. other messaging apps
Messaging apps aren’t all built the same. Differences in encryption, data collection, backups, and third-party features can affect how your data is handled. The comparison below highlights how WeChat stacks up against other major messaging apps in these areas.
| Signal | Telegram | |||
| E2EE | No | Yes (default for all messages and calls) | Yes (default for all messages and calls) | Optional (secret chats) |
| Chat data stored on company servers | Temporarily, depending on the message type. Favorited messages are stored until they are removed | No message content stored; limited metadata retained | No message content stored; limited metadata retained | Yes for cloud chats, but not for secret chats |
| Types of data collected | Account details, contacts (with permission), device info, location (if enabled), app activity, and Mini Program data. | Account details (like your phone number), technical data collected during use (such as connection and device information), and contact information shared by other users | Phone number and optional profile details. Minimal technical data needed to deliver messages. Contact data can be collected, but this is optional | Phone number and basic profile info, contacts (if synced), cloud chat history for non-secret chats, device and IP information, and metadata used for security and spam prevention |
| Account registration | Phone number required | Phone number required | Phone number required | Phone number required |
| Backups | No cloud backups, device-to-device chat migration only | Optional cloud backups, encryption depends on settings | Opt-in secure backups with E2EE; Signal cannot access backup contents | Yes, cloud-based by default |
| Third-party integrations | Large Mini Program ecosystem with separate data policies | No third-party integrations (business API only) | No third-party integrations | Smaller bot and service ecosystem |
Learn more: Don’t want to keep using WeChat? Find out how to delete your WeChat account.
FAQ: Common questions about WeChat
Does WeChat spy on users?
WeChat collects information needed to provide its services, such as account details, device information, and activity within the app. Its Privacy Policy also states it may share data with law-enforcement or regulatory bodies when required by applicable laws. The policy doesn’t describe surveillance or monitoring of users beyond these disclosures.
Is WeChat safe for payments?
WeChat Pay is generally considered safe for payments. It follows Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI-DSS) standards, which is widely used across the payment industry. The service also supports security measures such as biometric authentication, fraud detection, and password protection.
Is WeChat safe on iOS and Android?
WeChat is safe to download on both iOS and Android, but it isn’t 100% risk-free. As with other large messaging platforms, users may encounter phishing attempts, fake accounts, or malicious links. Keeping your device updated and being cautious with unknown users and Mini Programs can help reduce these risks.
How can you delete your data from WeChat?
You can request account deletion through the app’s settings. Deleting your account removes personal information associated with your profile, although WeChat notes that it may retain some data if required by local laws or for regulatory obligations. It may also take time for all associated information to be fully removed.
Should I uninstall WeChat if I’m concerned about privacy?
If you’re uncomfortable with the app’s data practices or the information it collects, uninstalling it is a straightforward way to limit further data access.
Is WeChat legal in the U.S.?
Yes. WeChat is currently legal in the U.S., so you can freely download and use the app.
Take the first step to protect yourself online. Try ExpressVPN risk-free.
Get ExpressVPN